Common Law Admission Test (CLAT)
Common Law Admission Test (CLAT) is a centralized test for admission to 21 National Law Universities in India. 43 other education institutes and two public sector institutes are also eligible to use these scores. The test is conducted by the 21 participating law schools in rotation, in the order of their establishment, starting with National Law School of India University which conducted CLAT-2008.
The test is taken after the Higher Secondary Examination or the 12th grade for admission to integrated under graduation programs in Law and after Graduation in Law for Master of Laws(LL.M) programs conducted by these law universities.
Eligibility & Age Limit
Undergraduate Program (Five Year Integrated LLB (Hons) Course)
- Candidates should be Passed 10+2 or equivalent examination with a minimum of (i) Forty Five percent (45%) marks in case of candidates belonging to Unreserved/OBC/Specially Abled Persons (SAP)/NRI/NRI sponsored categories and (ii) Forty percent (40%) marks in case of candidates belonging to SC/ST categories. Candidates appearing in the qualifying examination in March/April 2020 are also eligible to apply.
Age Limit
- Candidates should be below Twenty (20) years of age in case of Unreserved/NRI/NRI sponsored categories and below twenty-two (22) years in case of SC/ST /OBC/SAP categories as on 01st July 2020.
Post-Graduate Program (One Year LLM Course)
- Candidates must be LLB or equivalent degree examination with a minimum of Fifty Five percent (55%) marks in case of Unreserved/OBC/SAP categories and Fifty percent (50%) in case of SC/ST categories. Candidates appearing in the qualifying examination in April / May 2020 are also eligible to apply.
Exam Pattern for NVS Assistant Commissioner
For UG Courses
Subject | No. of Questions | Marks | Duration |
English using Comprehension | 40 | 40 | 2 hours |
General Knowledge / Current Affairs | 50 | 50 | |
Elementary Mathematics | 20 | 20 | |
Logical Reasoning | 40 | 40 | |
Legal Aptitude | 50 | 50 | |
Total | 200 | 200 |
Negative marking of 0.25 marks is allotted for incorrect answers.
For PG Courses
No. of Questions | Marks | Duration | |
Constitutional Law | 50 | 50 | 2 hours |
Jurisprudence | 50 | 50 | |
Other Law Subjects such as Contract, Torts, Criminal Law, International Law, Family Law, Property Law, IPR etc. | 50 | 50 | |
Total | 150 | 150 |
CLAT Syllabus
UG Program
- English including Comprehension: The English section will test the candidate’s proficiency in English based on comprehension passages and grammar. In the comprehension section, candidates will be assessed on their understanding of the passage and its central theme, meanings of words used therein, etc. The grammar section requires correction of incorrect grammatical sentences, filling of blanks in sentences with appropriate words, etc.
- General Knowledge and Current Affairs: The General knowledge will be evaluated on the general awareness including static general knowledge. Questions on current affairs will test the candidate’s on their knowledge of national and international current affairs.
- Mathematics: This section will test the candidate’s knowledge on elementary mathematics, i.e., maths taught upto 10th Class/Standard.
- Legal Aptitude: This section will test the candidate’s interest towards the study of law, research aptitude and problem solving ability. Questions may include legal propositions (described in the paper), and a set of facts to which the said proposition has to be applied. Some propositions may not be “true” in the real sense, candidates will have to assume the “truth” of these propositions and answer the questions accordingly.
- Logical Reasoning: The purpose of the logical reasoning section is to test the candidate’s ability to identify patterns, logical links and rectify illogical arguments. It may include a variety of logical reasoning questions such as syllogisms, logical sequences, analogies, etc. However, visual reasoning will not be tested.
List of 21 Participating National Law Universities ( NLUs)
- National Law School of India University, Bengaluru (NLSIU)
- National Academy of Legal Study & Research University of Law, Hyderabad (NALSAR)
- National Law Institute University, Bhopal (NLIU)
- The West Bengal National University of Juridical Sciences, Kolkata (WBNUJS)
- National Law University, Jodhpur (NLUJ)
- Hidayatullah National Law University, Raipur (HNLU)
- Gujarat National Law University, Gandhinagar (GNLU)
- Dr. Ram Manohar Lohiya National Law University, Lucknow (RMLNLU)
- Rajiv Gandhi National Law University, Punjab (RGNUL)
- Chanakya National Law University, Patna (CNLU)
- National University of Advanced Legal Studies, Kochi (NUALS)
- National Law University Odisha, Cuttack (NLUO)
- National University of Study & Research in Law, Ranchi (NUSRL)
- National Law University & Judicial Academy, Assam (NLUJAA)
- Damodaram Sanjivayya National Law University, Visakhapatnam (DSNLU)
- Tamil Nadu National Law School, Tiruchirappalli (TNNLS)
- Maharashtra National Law University, Mumbai (MNLU)
- Maharashtra National Law University, Nagpur (MNLU)
- Maharashtra National Law University, Aurangabad (MNLU Aurangabad)
- Himachal Pradesh National Law University (HPNLU) Ghandal, Shimla
- Dharmashastra National Law University, Jabalpur
Two public sector institutions
- Oil India
- Oil and Natural Gas Corporation
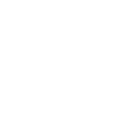
Success Dreams Education – Class Schedule ( For UG & PG CLAT)